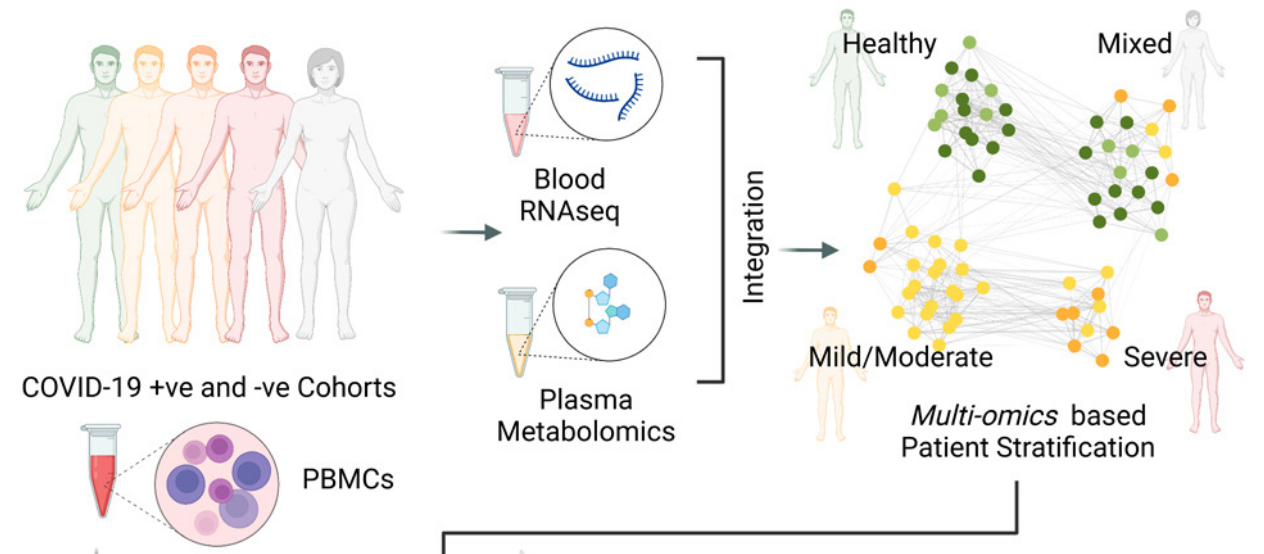
The clinical manifestation of COVID-19 is extremely diverse. Therefore, Swedish scientists using system-wide network-based system biology analysis characterized the main factors aggravating the severity of the disease on an individual and group level. The simultaneous interpretation of the results from transcriptomics of peripheral blood mononuclear cell, immunophenotyping, plasma metabolomics and monocyte metabolomics allowed scientists to identify genes encoding the SLC family of transporters and metabolites such as α-ketoglutarate, succinate, malate, and butyrate as important risk factors for severe COVID-19. The paper published in Cell Systems.
https://www.cell.com/cell-systems/fulltext/S2405-4712(22)00276-9#%20